Simulation conditions
Sometimes measurements are collected under different experimental conditions, which in the model correspond to simulating with different initial values and/or control parameter values.
This is handled via simulation conditions defined via PEtabCondition. This tutorial shows how to specify simulation conditions. As a running example, we use the Michaelis-Menten model from the starting tutorial:
using Catalyst, PEtab
sys = @reaction_network begin
@parameters S0 c3=3.0
@species begin
S(t) = S0
E(t) = 50.0
SE(t) = 0.0
P(t) = 0.0
end
@observables begin
obs1 ~ S + E
obs2 ~ P
end
c1, S + E --> SE
c2, SE --> S + E
c3, SE --> P + E
end
@parameters sigma
petab_obs1 = PEtabObservable(:petab_obs1, :obs1, 3.0)
petab_obs2 = PEtabObservable(:petab_obs2, :obs2, sigma)
observables = [petab_obs1, petab_obs2]
p_c1 = PEtabParameter(:c1)
p_c2 = PEtabParameter(:c2)
p_S0 = PEtabParameter(:S0)
p_sigma = PEtabParameter(:sigma)
pest = [p_c1, p_c2, p_S0, p_sigma]Defining simulation conditions
Simulation conditions are specified with PEtabCondition:
PEtab.PEtabCondition Type
PEtabCondition(condition_id, assignments::Pair...; t0 = 0.0)Simulation condition that overrides model entities according to assignments under condition_id.
Used to set initial values and/or model parameters for different experimental conditions. For examples, see the online package documentation.
Arguments
condition_id::Union{String, Symbol}: Simulation condition identifier. Measurements are linked to this condition via the columnsimulation_idin the measurement table.assignments: One or more assignments of the formtarget_id => target_value.target_id: Entity to assign (Symbol,String, or SymbolicsNum). Can be a model state id or model parameter id for a parameter that is not estimated.target_value: Value/expression assigned totarget_id. AString,Real, or a Symbolics expression (Num) which can use standard Julia functions (e.g. exp, log, sin, cos). Any variables referenced must be model parameters orPEtabParameters (model state variables are not allowed).
Keyword Arguments
t0 = 0.0: Simulation start time for the condition.
Specifically, each PEtabCondition defines a unique condition id (used to link rows in the measurement table) and one or more assignments of the form target_id => target_value. For example, assume two conditions: in :cond1, the initial value of E is 40.0 and the value of parameter c3 is 0.5, while in :cond2, E = 100.0 and c3 = 2.0:
cond1 = PEtabCondition(:cond1, :E => 40.0, :c3 => 0.5)
cond2 = PEtabCondition(:cond2, :E => 100.0, :c3 => 2.0)
simulation_conditions = [cond1, cond2]2-element Vector{PEtabCondition}:
PEtabCondition cond1: E => 40.0, c3 => 0.5
PEtabCondition cond2: E => 100.0, c3 => 2.0All conditions should be collected in a Vector. If a model state or parameter is not assigned in a given condition, its default value from the model is used.
Given simulation conditions, each measurement must be linked to a simulation condition via a simulation_id column in the measurement DataFrame (column names matter, but not order):
| simulation_id (str) | obs_id (str) | time (float) | measurement (float) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cond1 | petab_obs2 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| cond1 | petab_obs1 | 10.0 | 0.1 |
| cond2 | petab_obs2 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| cond2 | petab_obs1 | 20.0 | 1.5 |
Note that the ids in simulation_id must match the ids defined above with PEtabCondition. In Julia:
using DataFrames
measurements = DataFrame(
simulation_id = ["cond1", "cond1", "cond2", "cond2"],
obs_id = ["petab_obs2", "petab_obs1", "petab_obs2", "petab_obs1"],
time = [5.0, 10.0, 1.0, 20.0],
measurement = [0.7, 0.1, 1.0, 1.5],
)| Row | simulation_id | obs_id | time | measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| String | String | Float64 | Float64 | |
| 1 | cond1 | petab_obs2 | 5.0 | 0.7 |
| 2 | cond1 | petab_obs1 | 10.0 | 0.1 |
| 3 | cond2 | petab_obs2 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | cond2 | petab_obs1 | 20.0 | 1.5 |
Given a Vector of simulation conditions and measurements in the format above, a PEtabModel accounting for multiple simulation conditions can be created by passing the conditions via the simulation_conditions keyword:
model = PEtabModel(
sys, observables, measurements, pest;
simulation_conditions = simulation_conditions
)
petab_prob = PEtabODEProblem(model)Plotting the model solution under :cond1 and :cond2 shows the effect of the different condition settings (e.g. the initial value of E):
using Plots
x = get_x(petab_prob)
sol_cond1 = get_odesol(x, petab_prob; condition = :cond1)
sol_cond2 = get_odesol(x, petab_prob; condition = :cond2)
p1 = plot(sol_cond1, title = "cond1")
p2 = plot(sol_cond2, title = "cond2")
plot(p1, p2)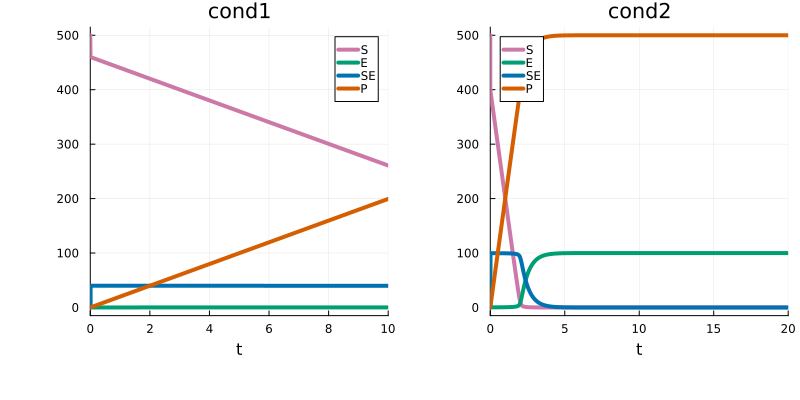
Simulation start time
By default, the model is simulated from t0 = 0.0 for each each simulation condition. This can be changed via the t0 keyword in PEtabCondition. For example, to simulate the model from t0 = 5.0 for :cond1:
cond1 = PEtabCondition(:cond1, :E => 0.0, :c3 => 0.5; t0 = 5.0)PEtabCondition cond1: E => 0.0, c3 => 0.5As seen by plotting, the simulation for :cond1 now starts at t = 5.0:
model = PEtabModel(
sys, observables, measurements, pest;
simulation_conditions = [cond1, cond2]
)
petab_prob = PEtabODEProblem(model)
x = get_x(petab_prob)
sol_cond1 = get_odesol(x, petab_prob; condition = :cond1)
sol_cond2 = get_odesol(x, petab_prob; condition = :cond2)
p1 = plot(sol_cond1, title = "cond1")
p2 = plot(sol_cond2, title = "cond2")
plot(p1, p2)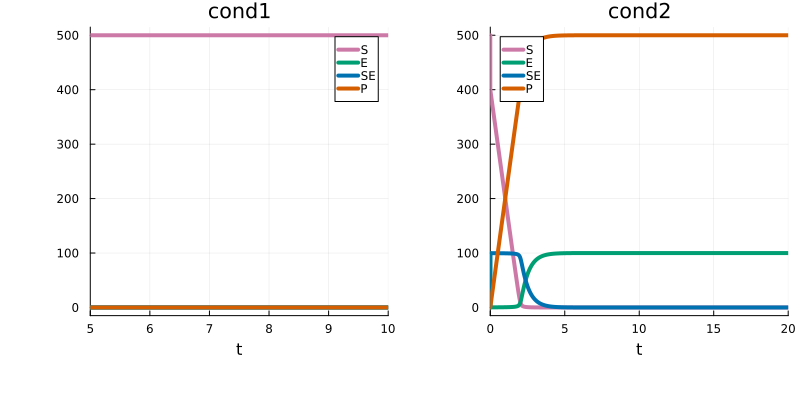
Change simulation start time without simulation conditions
If a model does not use simulation conditions, simulation start time can be changed by creating an empty condition: cond = PEtabCondition(:cond1; t0 = 5.0)